Introduction
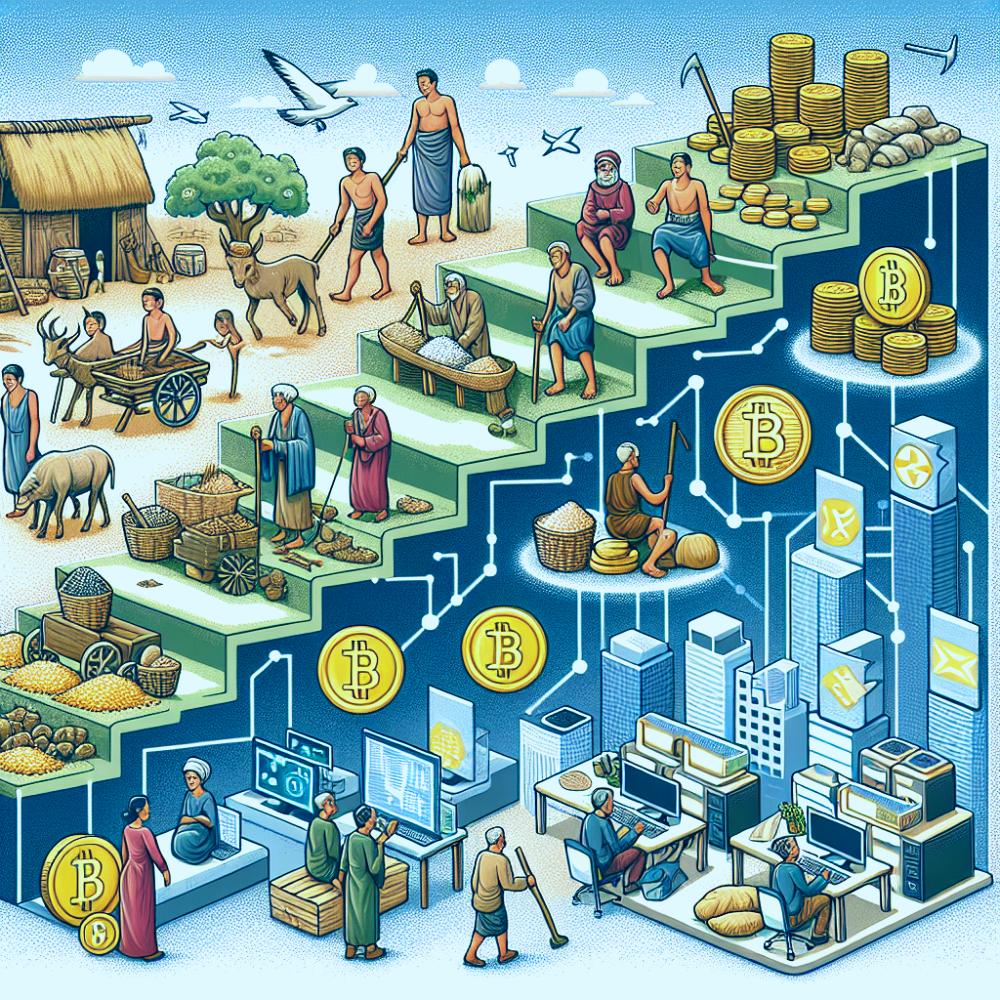
Money has been a critical part of human civilization, evolving with time to meet the changing needs of society. Its journey from the barter system to Bitcoin reflects the transformation of economic systems, technological progress, and societal changes.
The Barter System
The earliest form of trade was the barter system, which took place around 6000 BC. It involved the direct exchange of goods or services, without a medium of exchange like money. Livestock, grains, or commodities like precious metals were commonly traded. However, this system had its flaws. It required a 'double coincidence of wants', meaning both parties had to have what the other wanted. Also, determining the relative value of goods was a challenge.
Commodity Money
To overcome the limitations of the barter system, commodity money was introduced. This form of money had intrinsic value. Examples include gold, silver, copper, grains, and livestock. These commodities were accepted universally due to their inherent worth. However, they were not without shortcomings. Commodities were often cumbersome to transport, could depreciate in value, and were susceptible to theft.
Metallic Currency and Coinage
Around 1000 BC, China introduced the first known currency, which was made of base metal. Later, in 600 BC, the Lydians (in modern-day Turkey) introduced the first gold and silver coins. Coinage became a standard practice, and different civilizations started minting their coins with distinctive symbols. The value of these coins was determined by the type and amount of metal used. Coins had advantages over commodity money
they were portable, durable, divisible, and had a standardized value.
Paper Currency
The Chinese were also the first to use paper currency, beginning in the 7th century during the Tang Dynasty. Paper money was initially backed by gold or silver, but eventually, countries adopted the fiat system, where the value is not backed by a physical commodity. The convenience of paper money made it popular. It was lightweight, easy to carry and could represent larger values, making it ideal for an expanding economy.
Plastic Money - Credit and Debit Cards
The financial world saw another evolution with the introduction of plastic money in the mid-20th century. Credit and debit cards provided an electronic form of payment. They offered convenience, security, and ease of tracking transactions. These cards also facilitated online shopping, contributing to the rise of e-commerce.
Digital Money and Electronic Transfers
As technology advanced, so did the means of money transfer. Digital money refers to electronic storehouses of value, such as bank balances and online wallets. Electronic transfers allow for instant money transfer, anywhere, anytime, making transactions seamless and convenient. Services like PayPal, Venmo, and direct bank transfers have revolutionized the way we transact.
Cryptocurrency and Bitcoin
The latest evolution in the money timeline is cryptocurrency, a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Bitcoin, introduced in 2009, is the first and most popular cryptocurrency. It operates on a technology called blockchain, which is a decentralized technology spread across many computers that manage and record transactions. Cryptocurrencies offer the promise of lower transaction fees than traditional online payment mechanisms and are operated by a decentralized authority, unlike government-issued currencies.
Conclusion
The journey of money from barter to Bitcoin is a fascinating tale of societal needs, technological innovation, and economic development. As we step into the future, the concept of money will continue to evolve. Whether it's digital currencies, cryptocurrencies, or some yet unknown form, one thing is clear
money, in whatever form, will continue to be a fundamental pillar of human civilization.